5 frequently asked questions about the electric vehicle battery supply chain
“In order to promote a new, zero-emissions world, automakers have developed a wide range of electric vehicles, from airplanes to ships to cars, and each mode of transportation is studying the road to electrification. With the electrification of transportation and the continuous increase of batteries in energy storage applications, the battery supply chains of equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and utility companies have undergone fundamental changes.
“
The discussion around the electrification of transportation is intensifying all over the world…Governments are also formulating stricter standards for storage tanks.
In order to promote a new, zero-emissions world, automakers have developed a wide range of electric vehicles, from airplanes to ships to cars, and each mode of transportation is studying the road to electrification. With the electrification of transportation and the continuous increase of batteries in energy storage applications, the battery supply chains of equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and utility companies have undergone fundamental changes.
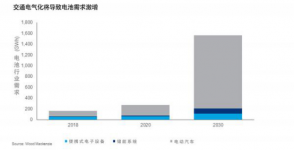
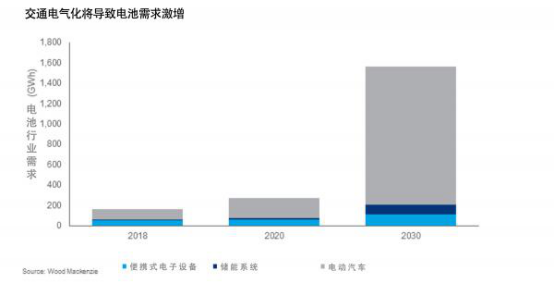
Wood Mackenzie predicts that by 2030 there will be 15 million electric vehicles. Some people even think that this is a more conservative growth rate. The future of electrification is not a small challenge for battery technology. The following roughly answers 5 questions in the field of electric vehicle battery supply chain.
1. What are the main components of electric vehicle batteries?
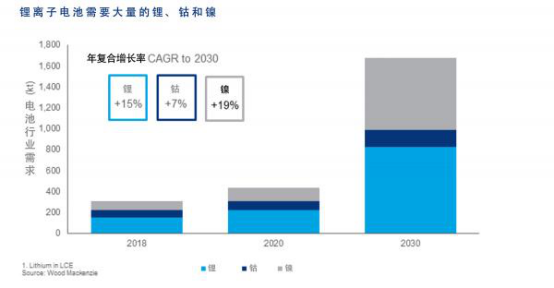
Battery energy density is critical to the success of electric vehicles. Innovations in battery technology enable consumers to use cars that are lighter, more energy efficient, cheaper, and last longer. Therefore, the demand for high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries will surge in tandem with the demand for electric vehicles themselves. Lithium-ion batteries require a large number of key metal substances, among which lithium, cobalt and nickel are the most critical. Of course, in China, lithium iron phosphate batteries that do not contain cobalt and nickel are more commonly used in specific transportation and energy storage fields.
2. Can the supply of battery raw materials keep up with the demand for electric vehicles?
The electrification of transportation is changing the demand and supply of battery raw materials. In fact, battery raw materials are expected to have double-digit growth rates in the next ten years. The latest research by Wood Mackenzie shows that by the mid-2020s, battery raw materials may face a supply squeeze, which will increase the pressure on the supply chain.
3. Where will the supply of lithium resources come from?
The supply of many basic resources in the world comes from areas with particularly high political, social, and environmental risks. For example, Iraq, which recently broke out an anti-American wave, ranks fourth in the world in oil reserves, but the unstable political environment has affected oil exports. There are also such risks in the supply of raw materials for lithium batteries, which increases the complexity of original equipment manufacturers’ procurement. In this regard, Australia is an exception. It has become the world’s largest source of lithium metal supply, and there is currently no major change in its lithium resource supply.
4. What are the potential threats to the exploitation of lithium resources?
Traditional brine operations in the lithium triangle of Chile, Argentina and Bolivia are the biggest challenges facing lithium supply. Can these water-consuming operations be scalable without causing lasting damage to the surrounding environment?
For cobalt, the supply situation is even more severe. In 2018, 72% of the world’s primary cobalt production came from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This war-torn country is better known for poverty, corruption and danger. The Ebola outbreak has even recently occurred and violence has also increased. It has had a great impact on the mining and transportation of cobalt in the country by enterprises of various countries. It is understood that BMW (BMW) has promised not to use cobalt from the Democratic Republic of Congo. The company’s cobalt raw materials will come from Australia and Morocco.
5. What are the alternatives to lithium-ion batteries?
In the first half of 2019, technology and transportation companies including Tesla and Samsung have invested heavily in the chemistry of replacing lithium-ion batteries, paying attention to the development of low-cobalt cathodes, solid electrolytes, and silicon-based anodes. Many battery companies are looking for other batteries that do not contain rare metals and have performance comparable to lithium-ion batteries, but such batteries are basically still in the laboratory research and development stage. Over time, some of these new technologies will begin to be commercialized to meet the growing demand for electric vehicles.
The Links: B141XG08-V3 SKM300GAL123D



